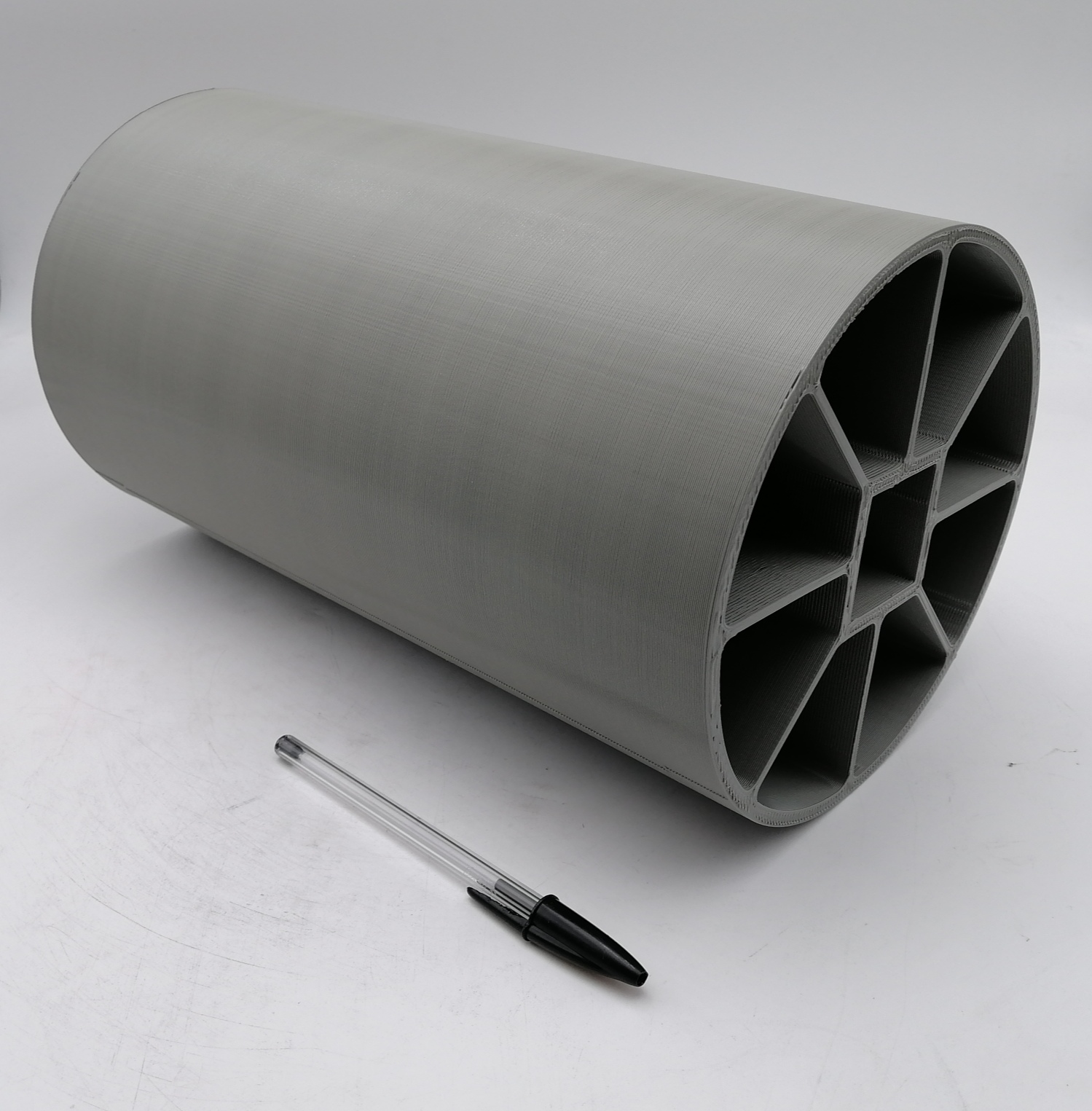
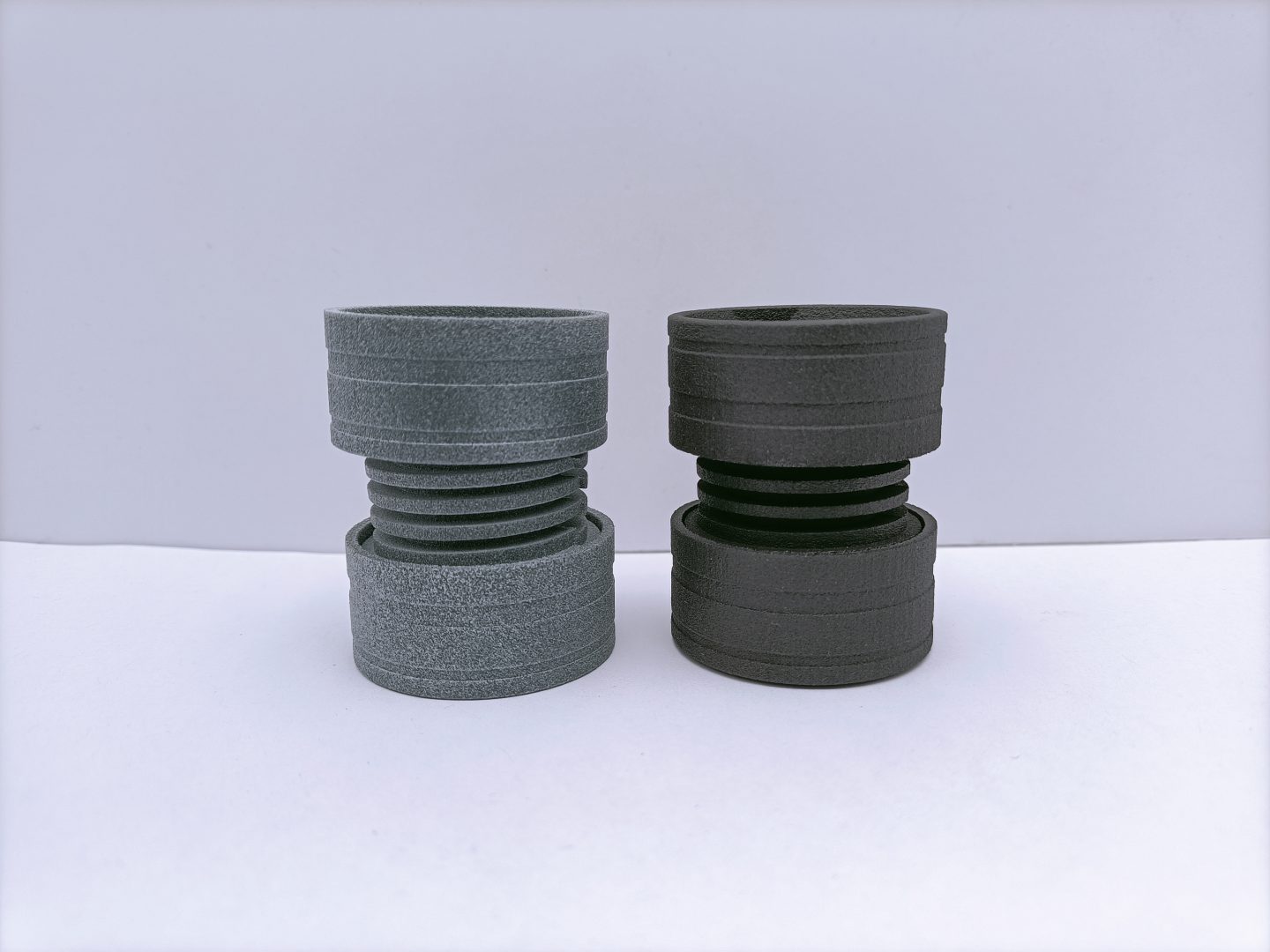
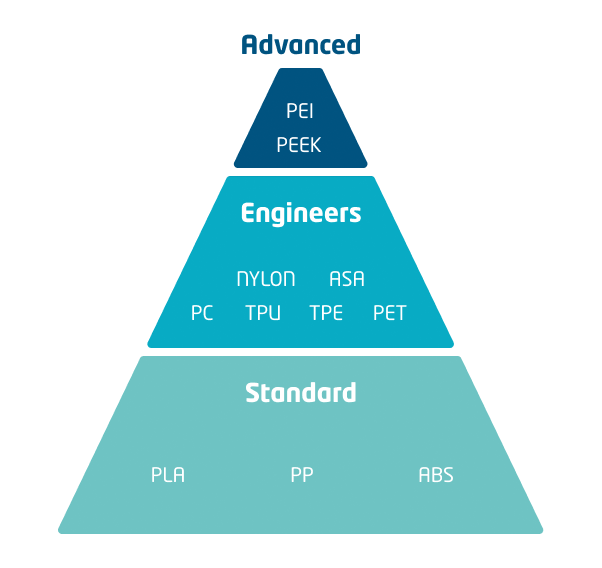
Plastic 3D printing
Thermoplastic polymers or plastics can be melted and solidified repeatedly while retaining their intrinsic properties. This is the characteristic utilized by the 3D printing technology known as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM). Plastic 3D printers using FDM melt a filament of a thermoplastic polymer to deposit it onto a previously deposited solid layer, so that the heat from the melted material re-melts the solidified layer to adhere both layers and form a single printed piece. This layer-to-layer adhesion is also promoted by the pressure exerted by the molten material exiting the 3D printer onto the solid layer.